
Back দমকল Assamese Ръчна помпа Bulgarian Bomba manual Catalan Schwengelpumpe German Bomba manual Spanish پمپ دستی Persian Pompe à bras French चांपाकल Hindi Ručna stapna sisaljka Croatian Kézi szivattyú Hungarian
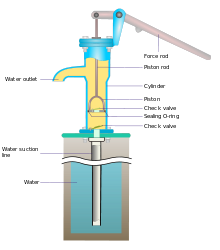



Hand pumps are manually operated pumps; they use human power and mechanical advantage to move fluids or air from one place to another. They are widely used in every country in the world for a variety of industrial, marine, irrigation and leisure activities. There are many different types of hand pump available, mainly operating on a piston, diaphragm or rotary vane principle with a check valve on the entry and exit ports to the chamber operating in opposing directions. Most hand pumps are either piston pumps or plunger pumps, and are positive displacement.[1]
Hand pumps are commonly used in developing countries for both community supply and self-supply of water and can be installed on boreholes or hand-dug wells.
- ^ "Handpumps". WaterAid. Retrieved 1 November 2010.